
We therefore need another way of handling this type of problems. But beware, on a fairly recent Macbook Pro with \(16\) Gb of memory, the computation literally stalled when the number of grid points in both direction was multiplied by \(2\). If you want to increase the precision, you need to refine the grid. We have collected some conclusive evidence that our procedure worked very nicely! Let’s use it to assess the precision of our solution: \ = pvec p = 0 p = 0 p = 0 p = 0 # Compute the exact solution p_e = p_exact_2d ( X, Y )Īt the beginning of the notebook, we have imported the l2_diff function from our module file module.py. Consider as an example the Poisson equation in three dimensions:

This is especially true when solving multi-dimensional problems. However, for very large systems, matrix inversion becomes an expensive operation in terms of computational time and memory. When the size of the matrix is not too large, one can rely on efficient direct solvers. Their implementation is a bit more complicated in the sense that they require the inversion of a matrix.
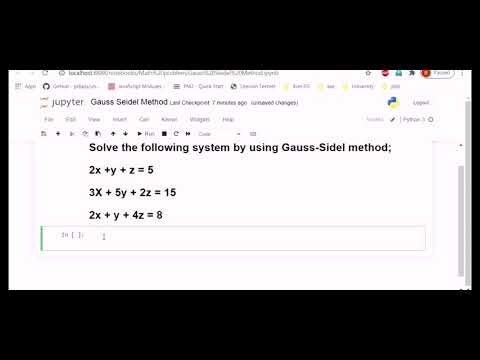
In the previous chapter we have discussed how to discretize two examples of partial differential equations: the one dimensional first order wave equation and the heat equation.įor the heat equation, the stability criteria requires a strong restriction on the time step and implicit methods offer a significant reduction in computational cost compared to explicit methods. insert ( 0, './modules' ) # Function to compute an error in L2 norm from norms import l2_diff % matplotlib inline To program the Gauss-Seidel method, we can use the following steps: Define the system of linear equations as a matrix equation AX B, where A is the. What mistakes did I make? I think it is in TriSolve method since if I replaced it with regular LU solver such as (np.linalg.solve) it works.Import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.sparse import diags import sys sys.

Below is the same implementation in MATLAB which works: function x = gSeidel(A,B,N) For some reason it is not converging even after 50000 iterations to the solution even when the matrix A is strict diagonal dominant. #O(n) per iteration, so overall O(nN), good for large SPD/SDD matricesĪ = np.array(,])Īns = is my Gauss-Seidel method in Python.
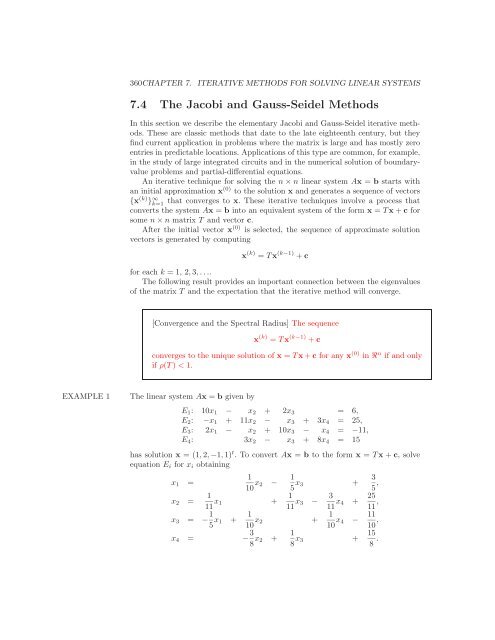
H is an iteration matrix that depends on A and B. Where x k + 1 and x k are approximations for the exact root of Ax B at (k + 1)th and kth iterations. The general iterative formulas can be given as: x k + 1 Hx k k 1, 2, 3. From scipy.linalg import solve_triangular as triSolve Iterative methods Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel in numerical analysis are based on the idea of successive approximations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
